Air bearings represent a cutting-edge technology that is transforming precision engineering across various industries. These innovative bearings utilize compressed air to create a thin film of air between surfaces, enabling frictionless motion and unparalleled precision.
Understanding Air Bearings
Air bearings, also known as aerostatic or air cushion bearings, are a type of bearing that relies on the principle of air lubrication to support and guide moving parts. Unlike traditional mechanical bearings, which use rolling elements or sliding surfaces, air bearings create a cushion of air between surfaces, eliminating contact and friction. This frictionless motion allows for ultra-smooth and precise movement, making air bearings ideal for applications requiring high levels of accuracy and control.
How Do Air Bearings Work?
- Air bearings operate by pressurizing a thin layer of air between a bearing surface and a mating surface, effectively lifting and supporting the load while allowing for frictionless motion.
- The compressed air is supplied through precision channels or grooves in the bearing surface, creating a uniform air film that separates the two surfaces.
- This air film provides support and stability, allowing for smooth and precise movement with minimal resistance.
Types of Air Bearings
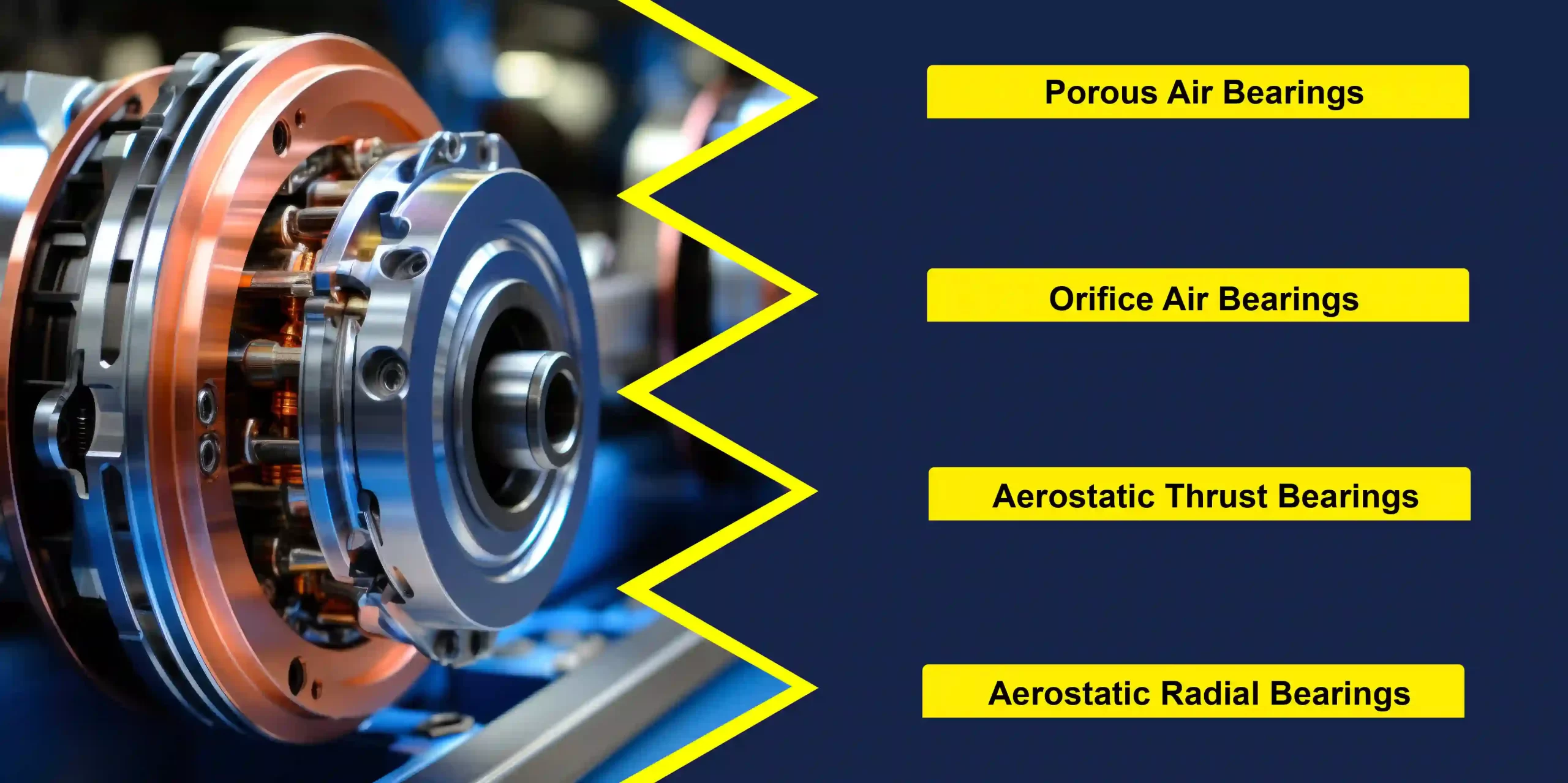
There are several types of air bearings, each designed for specific applications and operating conditions. The most common types include:
- Porous Air Bearings: These bearings use a porous material, such as porous graphite or sintered metal, to distribute air evenly across the bearing surface.
- Orifice Air Bearings: Orifice air bearings feature precision-drilled orifices through which compressed air is supplied to create the air film.
- Aerostatic Thrust Bearings: These bearings are designed to support axial loads and provide precise axial positioning without contact.
- Aerostatic Radial Bearings: Radial air bearings support radial loads and offer frictionless rotation for applications requiring high precision and accuracy.
Air Bearings Applications Across Industries

Air bearings find extensive use across various industries where precision, accuracy, and smooth motion are paramount. Some common applications include:
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: Air bearings are used in semiconductor manufacturing equipment, such as wafer handling systems and lithography machines, to provide ultra-precise positioning and control.
- Aerospace and Defense: In the aerospace and defense sectors, air bearings are employed in precision instruments, test equipment, and aerospace components to achieve high levels of accuracy and stability.
- Metrology and Inspection: Air bearings play a critical role in metrology and inspection systems, where they facilitate precise movement and positioning for dimensional measurement and quality control.
- Medical Devices: In medical device manufacturing, air bearings are utilized in equipment such as surgical robots and imaging systems to ensure smooth and precise motion during procedures.
Advantages of Air Bearings

Air bearings offer several key advantages over traditional mechanical bearings, including:
- Frictionless Motion: Air bearings eliminate friction and wear, resulting in ultra-smooth and precise motion with minimal resistance.
- High Precision: Air bearings provide exceptional accuracy and repeatability, making them ideal for applications requiring tight tolerances and precise positioning.
- Clean Operation: Since air bearings do not require lubricants, they offer clean and contamination-free operation, making them suitable for cleanroom environments and sensitive applications.
- Low Maintenance: Air bearings have fewer moving parts and do not require regular lubrication, reducing maintenance requirements and downtime.
Considerations of Air Bearings
While air bearings offer numerous advantages, there are also considerations to take into account when using them:
- Cost: Air bearings can be more expensive to manufacture and implement compared to traditional bearings, primarily due to the precision machining and control systems required.
- Complex Control Systems: Air bearings require sophisticated control systems to regulate air pressure and maintain optimal performance, which can add complexity to system design and operation.
FAQ's
What are air bearings used for?
Air bearings are used in a wide range of applications, including semiconductor manufacturing, aerospace and defense, metrology, medical devices, and precision engineering. They are ideal for applications requiring ultra-smooth motion, high precision, and clean operation.
What are the disadvantages of air bearings?
While air bearings offer numerous advantages, they also have some disadvantages, including higher cost, complexity of control systems, and sensitivity to contamination. Additionally, air bearings may require a constant supply of compressed air, which can increase energy consumption.
What is the pressure in an air bearing?
The pressure in an air bearing typically ranges from a few psi (pounds per square inch) to several hundred psi, depending on the specific application and load requirements. The pressure is carefully controlled to ensure optimal performance and stability of the bearing.
What is the speed of an air bearing?
The speed of an air bearing depends on various factors, including the type of bearing, air pressure, load, and operating conditions. In general, air bearings can support high-speed motion with velocities ranging from millimeters per second to several meters per second.
What are air bearings made of?
Air bearings are typically made of materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, or ceramics, depending on the application requirements. The bearing surfaces may be coated or treated to enhance wear resistance and reduce friction.
Which is better: air bearing or mechanical bearing?
The choice between air bearings and mechanical bearings depends on the specific application requirements and operating conditions.
- Air bearings offer advantages such as frictionless motion, high precision, and clean operation, making them suitable for applications requiring ultra-smooth motion and tight tolerances.
- However, they may be more expensive and require more complex control systems compared to mechanical bearings.
What is the efficiency of an air bearing?
The efficiency of an air bearing refers to its ability to convert input energy into useful output motion with minimal losses. Air bearings are known for their high efficiency due to their frictionless operation and minimal energy dissipation.
However, efficiency can vary depending on factors such as air pressure, load, and operating conditions, so it’s essential to optimize system design and control for maximum efficiency.