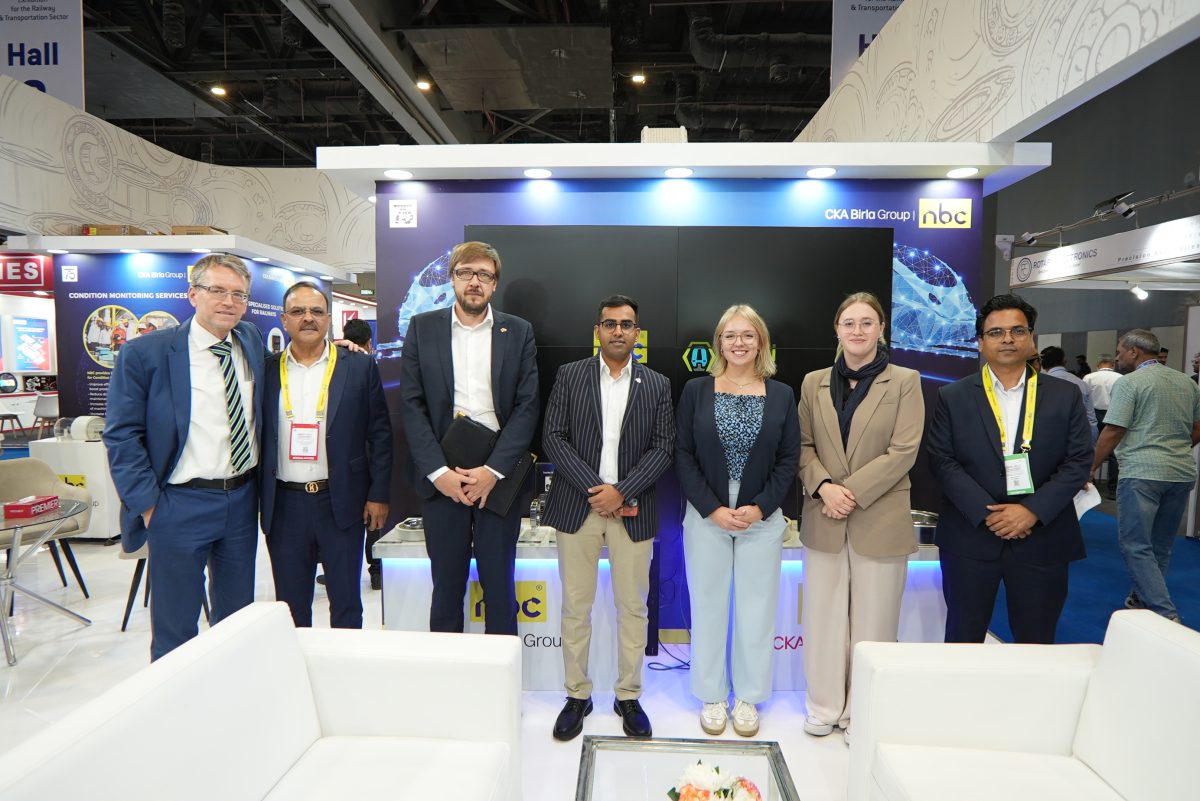
Delhi – October 15, 2025 – National Engineering Industries Ltd. (NEI), India’s leading bearings manufacturer under the NBC brand, and iMRail Technology GmbH, a pioneer in next-generation railborne mobility solutions, today announced a strategic partnership. This partnership lays the foundation for a comprehensive ‘Make in India’ ecosystem for advanced transit systems, including low-to-medium speed Maglev, next-generation Monorail and Ropeways as well as sub-systems for such mobility solutions.
Driving the Future of next-gen Mass Transit Applications
The collaboration between NEI and iMRail marks a significant milestone in NEI’s expansion beyond its core bearings expertise into advanced mobility systems. Leveraging iMRail’s cutting-edge technologies, the partners will deliver integrated, sustainable, and high-performance solutions to rail operators, OEMs, and urban transit developers across India and beyond.
Key focus areas:
- Breakthrough technologies: Joint development and deployment of non-conventional systems like Maglev, Monorail, and Ropeways.
- Sustainability and economic efficiency: Emphasis on environmentally responsible solutions that enhance performance and energy efficiency.
- Technological integration: Leveraging intelligent systems and digital innovation to redefine modern transportation.
Mr. Rohit Saboo, President & CEO, NEI (NBC Bearings) said, “This pivotal step in our journey toward next-generation mobility is immediately bolstered by the strategic agreement. We’re moving beyond mechanical components to deliver complete, intelligent systems, perfectly positioned to provide the foundational technology needed to realize India’s futuristic vision for Maglev, Monorail, and other mobility solutions.”
Maxim Weidner, CEO of iMRail Technology GmbH added, “Partnering with NBC Bearings gives us the scale and reach to rapidly deploy our innovative technologies. Together, we’re shaping a future of resilient, accessible, and sustainable mobility for tomorrow’s cities and beyond”
About NBC Bearings (NEI)
Founded in 1946, National Engineering Industries Ltd. (NEI) is the manufacturer of the NBC Bearings brand and a core part of the multi-billion-dollar CKA Birla Group. NEI is India’s leading manufacturer and exporter of bearings, known for superior quality and precision, and is the only bearing manufacturer in the world to have received the prestigious Deming Grand Prize (Japan). NEI has been serving the Indian Railways since 1952.
About iMRail
iMRail is a German technology-driven company specializing in the system integration and technical application of advanced urban transport systems, including elevated transit and specialized mass transit technologies. Its mission is to advance sustainable transportation through next-gen mobility innovations designed to make cities smarter, greener, and more connected.