RFQ of 3PL Warehouse







A retaining ring, also known as a circlip or snap ring, stands as a fundamental yet often overlooked component in the realm of fasteners. Its primary function is to secure various elements axially on a shaft or within a bore. Unlike traditional fastening methods such as threads or bolts, retaining rings provide a cost-effective and efficient solution for axial component retention.
Retaining rings find application in engineering and manufacturing processes due to their unique ability to streamline the fastening process while ensuring structural integrity. Unlike traditional fastening devices that often involve intricate threading or complex mechanisms, retaining rings provide a simpler yet highly effective solution. The key advantage are:
Overall, the decision to use retaining rings is driven by the desire for a practical and reliable fastening solution. Whether in manufacturing, repair, or assembly processes, the simplicity and effectiveness of retaining rings make them a valuable component, simplifying the complex task of securing elements in a wide range of applications.
The manufacturing process of retaining rings varies based on factors like type and size. Stamping, coiling, and machining are common methods employed in their production. These methods ensure precision and durability, aligning with the stringent requirements of diverse applications.
Retaining rings find extensive applications across various industries. Their usage spans from automotive and industrial settings to machinery applications. Common scenarios include securing bearings, gears, pulleys, or other rotating components on shafts.
The material selection for retaining rings depends on the specific demands of the application. Carbon steel, stainless steel, or various alloys are commonly utilized to ensure the rings withstand the mechanical stresses and environmental conditions they might encounter.
Retaining rings, though seemingly unassuming, play a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity of diverse mechanical assemblies. Their versatility, coupled with reliability, positions them as indispensable components across a myriad of industries. This comprehensive exploration aims to shed light on the intricacies of retaining rings, offering valuable insights into their types, materials, and applications, empowering engineers and enthusiasts alike in optimizing their usage for diverse engineering scenarios.
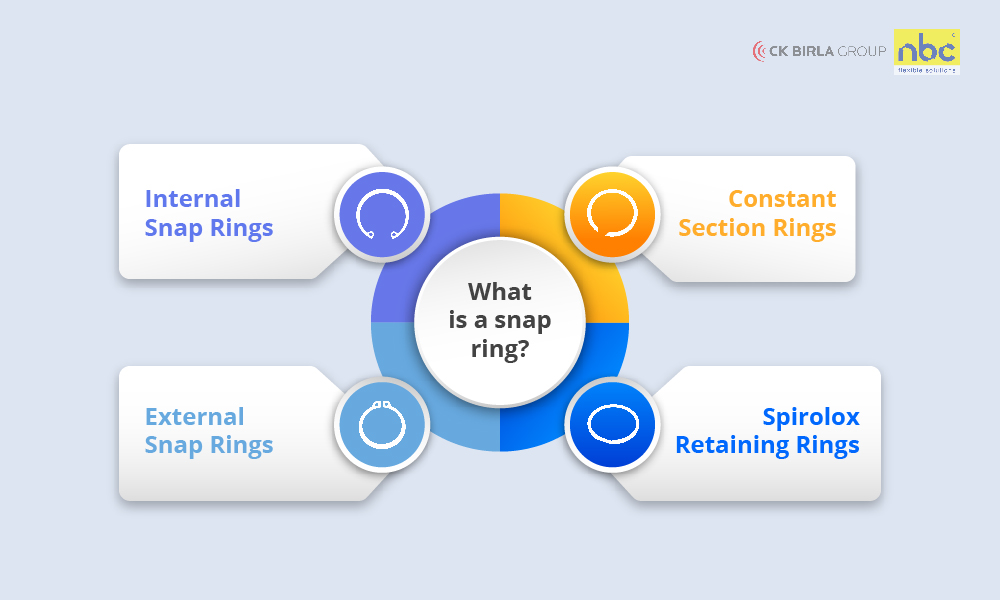
Retaining rings go by various names, and two commonly used alternatives are “circlips” and “snap rings.”
Retaining ring pliers serve as specialized tools meticulously crafted for the efficient installation or removal of retaining rings. These pliers have distinct tips and features designed to securely grip and manipulate the retaining ring during the installation or removal process.
In engineering terminology, “circlip” and “retaining ring” are often used interchangeably, essentially denoting the same type of fastener. Both terminologies refer to a versatile, ring-shaped device used for securing components onto a shaft or within a bore.
The measurement of retaining rings involves determining their nominal size, which corresponds to the shaft or bore diameter they are intended to fit. This measurement is critical for ensuring a precise and secure fit during the installation process.
The installation of retaining rings requires specialized tools, with retaining ring pliers being a commonly employed instrument. These pliers are tailored to provide a secure grip on the ring, facilitating seamless installation or removal. Additionally, other tools designed for specific retaining ring types may be utilized, ensuring the process aligns with industry standards and safety practices.

In the complex domain of automotive engineering, specific components work silently to guarantee smooth vehicle functionality. Among these essential contributors, wheel bearings play a crucial role in ensuring efficiency and safety.
A wheel bearing, at its core, is a compact yet critical component that facilitates the smooth rotation of the wheel hub assembly. This unassuming element bears the weight of the vehicle while ensuring minimal friction for optimal performance. Comprising an inner and outer ring, rolling elements (balls or rollers), and a cage to retain these elements, a wheel bearing is a precision-engineered assembly designed for reliability.
This precision-engineered assembly is designed with meticulous attention to detail, considering factors such as load-bearing capacity, durability, and operational efficiency. The synergy of these components allows wheel bearings to withstand the demands of vehicular motion while providing reliable and consistent performance.
In cars, wheel bearings silently ensure a smooth journey. As technology advances, they stay reliable under the vehicle, supporting its efficiency. Like a silent force, these components keep every ride dependable, embodying resilience.
It is not recommended to drive with a bad wheel bearing as it can lead to further damage and compromise safety. Prompt replacement is advised.
Yes, worn down wheel bearings can impact the effectiveness of the brake system leading to
The lifespan of wheel bearings varies, but they typically last between 85,000 to 100,000 miles. Regular maintenance and early detection of issues can further extend their longevity.
Factors such as heavy loads, poor-quality lubrication, water exposure, or simply wear and tear over time can contribute to the deterioration of wheel bearings.
Wheel bearing noise is often a humming or grinding sound that increases with vehicle speed. It is a common sign of a potential issue and should be addressed promptly to avoid further damage.