Choosing the right bearing is like building a strong foundation – everything else depends on it!
In the same vein, bearing pullers are crucial for safely removing parts like bearings, gears, and pulleys from a shaft or a recess.
We’re all aware of the importance of bearing and how choosing the right one ensures the overall efficiency of machines. However, bearings are required to be replaced, some due to damage, premature failure, or when they naturally wear out, a bearing puller ensures that the replacement is done correctly. The bearing puller also makes it easier to remove bearings from complex and tight spaces in mechanical systems. Around 50 million bearings are replaced annually, and bearing pullers guarantee the correct replacement of the crucial part.
Introduction to Bearing Pullers
A bearing puller is a specialised equipment designed for the removal of bearings from shafts, housings, or other mechanical components. The puller ensures the components and parts are removed without causing damage. The bearing puller is designed to operate in confined spaces and allows technicians to extract the bearings, gears, pulleys, etc. while avoiding damage to surrounding parts and reducing machine downtime.
When it comes to bearings, brute force isn’t the answer – a bearing puller ensures effective dismounting. The same is true for bearing removal, particularly when a damaged or failed component needs to be removed quickly to minimise downtime. Without the proper tools, even a simple task can become difficult. Additional downtime may result from alternative removal methods that may damage nearby parts or components.
Working of a Bearing Puller
- Attachment and Setup: The puller is positioned to grip the bearing with specifically designed jaws.
- Force Application: The centre screw is turned or the hydraulic system is activated pushing the shaft and pulling the bearing outwards.
- Extraction: The bearing is gradually removed from its position without damaging the surrounding components.
There is a direct correlation between the use of a bearing puller and the overall performance of machinery. A puller contributes to optimal performance and reliability by ensuring that the bearing is removed effectively without damage, preventing unnecessary wear, reducing downtime and extending the equipment lifespan.
Types of Bearing Pullers
There are various types of bearing pullers, each designed to address specific maintenance needs, ensuring the safe and efficient removal of bearings in various applications.
- External Bearing Puller: This type of bearing puller is recommended when there is access to the external diameter (bearing’s back). External bearing pullers have the maximum reach and spread. External bearing pullers are of two types:
- Two-Jaw Pullers: These pullers are compact in size and are used for easy-to-move bearings.
- Three-Jaw Pullers: Three-jaw pullers are known for better stability and stronger grip and are used for more stubborn bearings.
- Internal Bearing Puller: Internal bearing pullers are designed for bearings seated inside the housing. Also known as a blind bearing puller, this type of puller grips the inner race or bore of the bearing to extract it.
- Hydraulic Puller: These pullers use hydraulic force and are known for high precision and greater pulling power. Hydraulic pullers are recommended for large or tightly fitted bearings that require significant force to remove.
- Bearing Separators: Bearing separators have a split design that surrounds the bearing creating space between the bearing and its mount. Such pullers are recommended for removal of bearing where there is limited space between the back of the bearing and other components of the machinery and where conventional pullers may not fit.
Comparison Chart for Different Types of Bearing Pullers
|
Feature |
External Pullers |
Internal Pullers |
Hydraulic Pullers |
|
Primary Use |
Bearings are removed by gripping the outer race |
Bearings are removed by gripping the inner race or bore |
Bearings are removed through hydraulic force from large or tightly fitted bearings |
|
Design |
Two or three adjustable arms for gripping |
Arms or jaws designed to expand inside the bearing |
Hydraulic cylinder applies precise force |
|
Applicability |
External bearings with easy access |
Bearings seated inside housings |
Heavy-duty applications & large bearings |
|
Force Application |
Manual, through a centre screw |
Manual, through a centre screw or hammer |
Hydraulic pressure for high force |
|
Ease of Use |
Simple, most commonly used |
Slightly complex due to internal access |
Requires skill to operate hydraulic systems |
|
Precision |
Moderate precision, risk of damaging the outer race |
High precision, grips securely from inside |
Very high precision, offers controlled & powerful removal |
Applications of Bearing Pullers

Automotive Industry
Automotive industry heavily relies on bearings, specifically ball bearings. Bearings are used in engines, wheels, axles and other applications to guarantee smooth operation. Because bearings are an essential part of every moving part of a vehicle they are subjected to a great deal of stress from intricate mechanical systems and constant usage, leading to wear and tear over time. Bearing pullers are the ‘go-to tool’ for replacing and maintaining these bearings which are typically located in complex and tight spaces. The pullers help technicians remove and service the components without causing damage to the nearby parts. Bearings are used in vehicles across various components, like wheels, engines, gearboxes, transmissions, electric motors, pumps, etc. External pullers – Two-jaw and three-jaw pullers are most commonly used in the automotive industry.
Industrial Machinery
Industrial machinery like motors, conveyors, pumps, and gearboxes across factories and production lines rely on bearings for efficient performance. Bearing pullers are utilised for regular inspection, servicing, and replacement of bearings to prevent downtime, optimise productivity, and avoid costly repairs.
Heavy Equipment
Bearings are essential to the effective operation of mining, construction, agricultural equipment and other heavy equipment. Because of the extreme stress they endure the bearings in these machines wear out frequently necessitating routine maintenance or replacement. Hydraulic bearing pullers are commonly used for heavy equipment due to their high pulling force and precision. A variety of heavy machinery including excavators, bulldozers, loaders, conveyor systems, crushers, tractors, harvesters and more bearing pullers are essential tools. Longer equipment lifespan, smooth operation and less downtime are all ensured by bearing pullers and their capacity to withstand the demanding requirements of heavy-duty applications.
How to Choose the Right Bearing Puller?
Similar to how choosing the correct bearing is crucial for efficient and safe operation choosing the correct bearing puller is also crucial for effective performance. When using the correct puller the bearing can be removed correctly without causing any harm to the nearby parts or components. However, there are several things to take into account when selecting the best bearing puller.
- Application and Bearing Type: When choosing the appropriate bearing puller it is important to consider both the bearing type and its particular application. External bearing pullers (two or three jaws) can be used to replace externally mounted bearings while internal bearing pullers are the recommended type for bearings inside the housing or bores and hydraulic bearing pullers are used for large and tightly fitted bearings.
- Bearing Size & Capacity: When selecting a bearing puller it’s critical to make sure the shaft diameter and bearing size are appropriate. A mismatch may result in ineffective work or harm to the surrounding elements. Additionally, for versatility adjustable pullers can be used to handle a variety of sizes.
- Material & Durability: Two of the most important factors to consider when choosing a bearing puller are build quality and durability. Selecting pullers composed of materials with high strength guarantees dependability and durability.
- Load Requirements: The load requirement must be taken into account when choosing a bearing puller i.e. large bearings or heavy machinery may require the use of a puller with a high load capacity such as a mechanical or hydraulic puller. On the other hand, lightweight pullers are adequate for applications that are less demanding or for bearings with low weight.
- Accessibility: The selection of the right bearing also depends on the space around the bearing. If the space around the bearing is limited, use bearing pullers with slim arms or two jaw pullers.
- Frequency of Use: If maintenance is occasional or done in long intervals basic mechanical puller might suffice, while if there is frequent usage or applicability for heavy-duty investing in a high-quality hydraulic puller is more cost-effective.
Using a Bearing Puller?
For a bearing to be removed effectively without causing damage to the surrounding components a bearing puller must be used correctly. Here is a detailed guide on using bearing pullers.
Step 1: Get the Work Place Ready
Disconnect the power source, ensure the machine is in a stationary position and put on safety gear like goggles and gloves.
Step 2: Determine the Type of Bearing
The second step is to identify the type of bearing to be removed/replaced i.e. internal or external. Further choose the right puller based on the bearing size, type, and location.
Step 3: Position the Puller
Put the puller jaws around the outer race for an external bearing and into the inner race in case of an internal bearing.
Step 4: Fasten the Puller
Tighten the puller and make sure it is in line with the shaft or housing to ensure a secure hold on the bearing.
Step 5: Apply Force
For manual pullers rotate the central screw to exert pressure and for hydraulic pullers turn on the hydraulic mechanism.
Step 6: Remove the Bearing:
Once the bearing is loose remove the bearing from the shaft or housing. Examine the bearing to ascertain whether it needs to be replaced.
Maintenance of Bearing Pullers

Proper maintenance of the bearing puller is necessary for its longevity, dependability, and safe operation. The following procedures guarantee the puller’s longevity and effectiveness.
- Regular Cleaning: The most important step in the maintenance of pullers is cleaning or removing the debris, grease, dirt, etc after usage. A mild cleaner or manufacturer-recommended cleaner should be used to avoid damage. Additionally, ensure the puller is dry before storing it to prevent rust or corrosion.
- Lubrication: The way lubrication leads to the effective performance of bearings, similarly lubrication of bearing pullers especially central screws, hydraulic fittings, etc ensures reduced friction and ensures smooth operation. Additionally for hydraulic pullers check for fluid levels and replace or refill if necessary.
- Storage Tips: The overall dependability and durability of bearing pullers are significantly impacted by storage. Pullers need to be cleaned and dried completely before being stored. The puller should ideally be kept in a dedicated case to prevent rust and other damage. Proper storage ensures extended lifespan, improves readiness, and enhances safety.
Bearing pullers must also be regularly checked for damages, especially the jaws – they may have signs of bending and cracking which may require replacement to avoid accidents. Also, inspection of threads on the screw or rods is equally important, as stripped or worn-out threads may compromise functionality. For hydraulic pullers the hoses, seals, and pumps must be checked for leaks and damages.
Advantages of Using Bearing Pullers
Using bearing pullers instead of traditional methods offers numerous benefits. Some of them are listed below:
- Efficient Bearing Removal: Compared to manual methods, bearing pullers enable quick and hassle-free bearing removal. It also reduces the physical strain required to disassemble tightly fitted or stuck bearings.
- Prevents from Damage: Bearing pullers are known and widely used for safely extracting the bearings without damaging the shaft, housing, or surrounding parts.
- Enhances Safety: Using bearing pullers eliminates the need for hammers or chisels which can be hazardous, additionally, pullers offer a controlled and secure grip, reducing the chance of tool slippage.
- Improves Maintenance Efficiency: Bearing pullers help speed up maintenance tasks, reducing downtime for machinery.
- Cost Effective: When removing expensive machinery parts pullers help prevent unintentional damage. They also reduce replacement costs by preventing the needless replacement of damaged shafts or bearings brought on by incorrect removal methods.
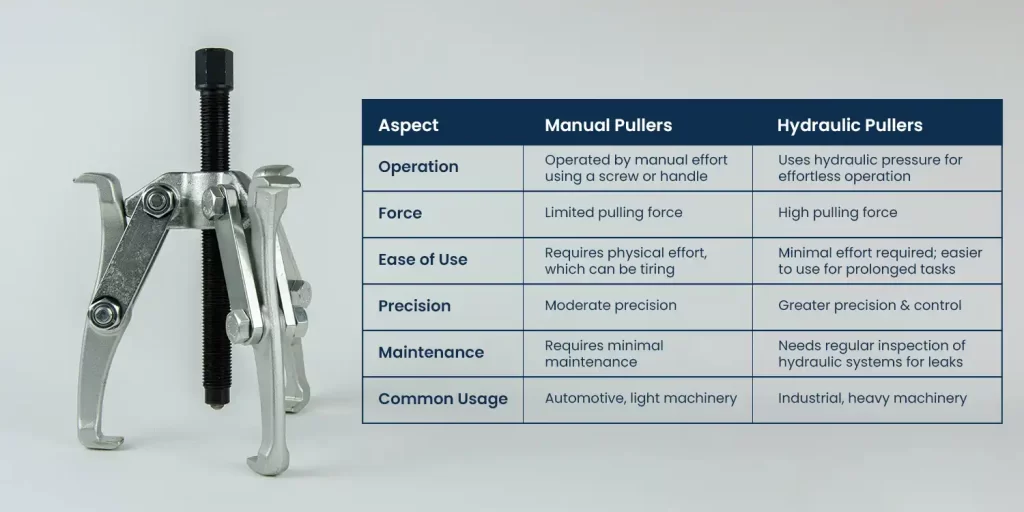
Manual Vs Hydraulic Bearing Pullers
FAQ's
What is the function of a puller?
A bearing puller is a specialised equipment designed for the removal of bearings from shafts, housings, or other mechanical components.
What is a bearing tool?
A bearing tool is a specialised tool used to remove bearings, gears, and other components from a shaft or recess
What is the method of removing the bearing?
Removing bearings is done through a bearing puller which ensures it is removed effectively without damaging the surrounding parts. The method of removal depends upon the type and size of the bearing.
How to select a bearing puller?
A bearing puller’s selection depends on various factors like the type of bearing, size, capacity, material, load requirement, etc.
How do you remove a bearing puller?
A bearing puller can be removed by loosening the screw shaft and turning it anticlockwise.
How to extract a small bearing?
A small bearing can be extracted through a compact or small bearing puller with two or three jaws