A Comprehensive Guide to Greases in the Bearing Industry
Bearings are crucial components in a wide range of machinery, from industrial equipment to automotive systems. The proper lubrication of these bearings is essential to ensure their smooth operation, longevity, and overall performance. Greases play a vital role in this lubrication process, providing a barrier that reduces friction, protects against corrosion, and aids in heat dissipation. In this blog, we’ll explore the different types of greases used in the bearing industry, their applications, and how to select and maintain them for optimal performance.
What is Grease? Why is it important for bearings?
Grease is a semi-solid lubricant composed of a base oil, thickener, and additives.
- It serves as a friction reducing component for the smooth movement of bearing elements protecting them from wear.
- Unlike oils, these are stable and less prone to leaking, making them ideal for cases where liquid lubricants are less effective.
- It forms a protective layer against contaminants like dust, water, and chemicals, therefore enhancing longevity.
- Grease prevents metal to metal contact to maintain alignment of the bearing components.
Good grease is especially important in high-load, high-speed applications where the stress on the bearings is significant. This directly protects against
- excessive friction,
- increased wear,
- overheating, and
- bearing failure.
What are the types of greases for bearings?

- Lithium-Based Greases: They offer excellent water resistance, good mechanical stability, and a wide operating temperature range. The lithium soap provides a consistent and smooth texture that adheres well to the bearing surfaces.
- Synthetic Greases: Synthetic base oils formulation delivers superior performance compared to conventional mineral-based greases. Designed for extreme conditions, they ensure thermal stability, low-temperature fluidity, and resistance to oxidation. Perfectly suited for long-term lubrication in harsh environments.
- Specialty Greases: Specialty greases are tailored for specific applications that require unique properties. High-Temperature resistance of up to 250°C or higher, making them suitable for use in furnaces, kilns, and other high-heat environments. Similarly Low-Temperature tenacity to remain fluid and effective at up to -50°C, for use in cold climates and refrigeration systems. Finally, Food-Grade formulation grease for non-toxic and safe use in food processing and packaging equipment.
Applications of Bearing Greases
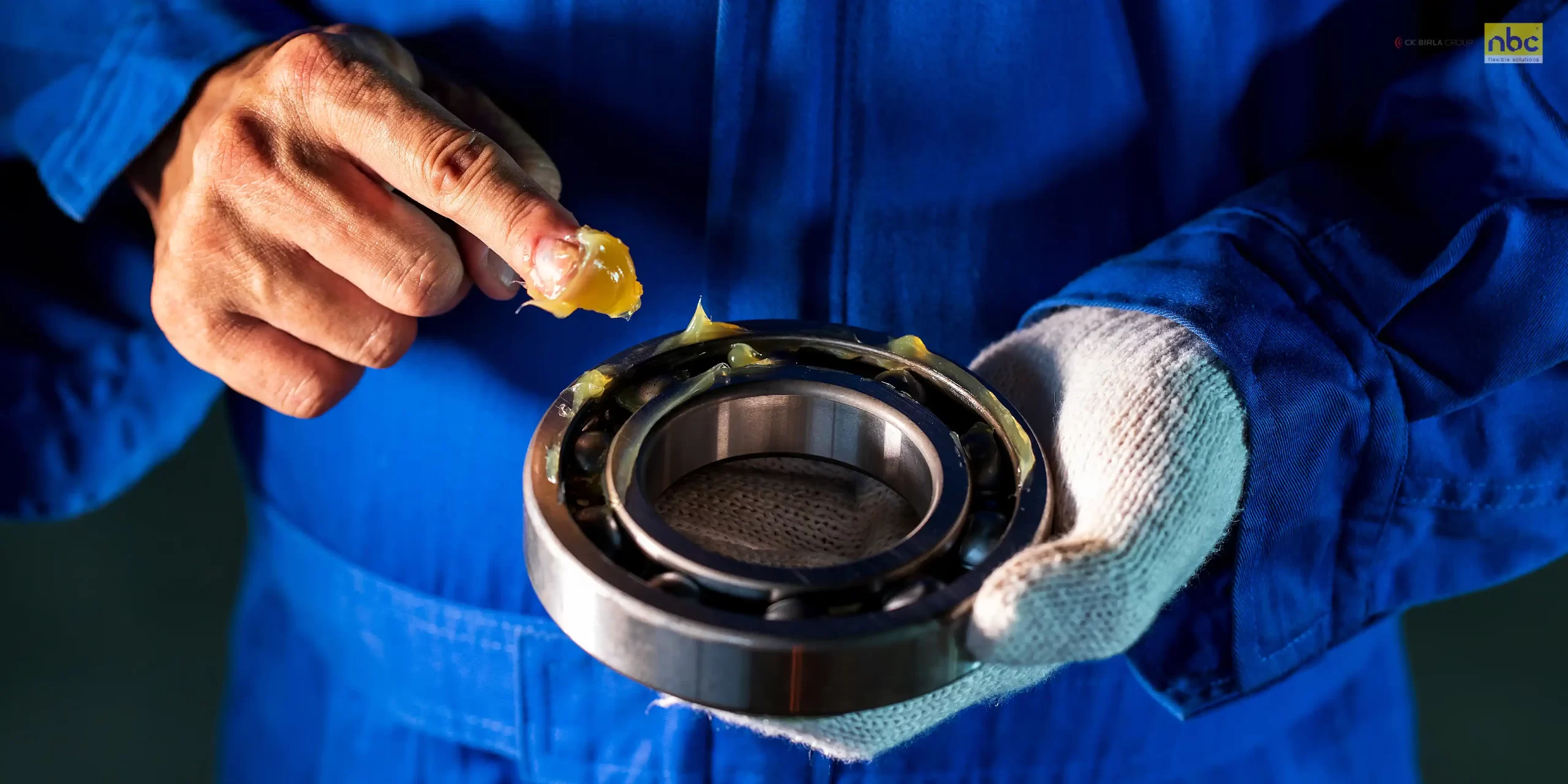

- Automotive Industry: Particularly useful in the lubrication of wheel bearings, electric motors, and other moving parts.
- Industrial Machinery: Greases must be able to withstand extreme pressures and temperatures while providing consistent lubrication to conveyor systems, compressors, and manufacturing equipment.
- Aerospace: Greases that can perform reliably under extreme conditions, including high altitudes, varying temperatures, and intense pressures. Specialised synthetic greases ensure safety, reduce maintenance needs, and enhance performance.
- Food and Beverage Industry: In this industry, hygiene is paramount. These are used in processing and packaging equipment to ensure that they do not contaminate the food products, have non-toxic formulations and meet strict regulatory standards.
Selecting the Right Grease for Bearings

Key Factors: When selecting grease for bearings, several factors must be considered:
- Load: The weight and force exerted on the bearings affect the type of grease required.
- Speed: High-speed applications demand greases with low viscosity to reduce friction.
- Temperature: The operating temperature range influences the choice of grease, with some formulations better suited to extreme heat or cold.
- Environment: Exposure to water, dust, chemicals, or other contaminants may necessitate the use of specialty greases.
- Bearing Type: The design and material of the bearing also play a role in determining the best grease.
Selection Conditions:
- Identify the operating conditions such as load, speed, temperature, and environment.
- Choose the appropriate grease based on the conditions where the bearing is used.
- Consult manufacturer recommendations, i.e. refer to NBC Bearings manufacturer’s guidelines for grease selection to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
Maintaining Greased Bearings
Routine Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of greased bearings. This includes
- routine inspections,
- cleaning, and
- re-greasing according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Signs of Insufficient or Excessive Grease: Over-greasing can lead to excessive heat and energy loss, while under-greasing can cause increased friction and wear. Common signs of lubrication issues include
- unusual noise,
- increased operating temperature, and
- visible leakage.
Cleaning and Regreasing: When cleaning bearings, use a solvent to remove old grease and contaminants. Once cleaned, apply a fresh layer of grease, ensuring it reaches all critical areas.
Performance and Reliability of Greases
Performance Metrics: The performance of grease is measured by its
- ability to reduce friction,
- resist oxidation, and
- maintain consistency under varying conditions.
High-quality greases contribute to improved bearing efficiency, reduced wear, and extended service life.
Testing and Quality Control: Greases undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet industry standards for performance and reliability. This includes tests for
- consistency,
- thermal stability, and
- resistance to contamination.
Troubleshooting: Common issues related to grease performance include
- excessive wear,
- leakage, and
- noise.
Identifying and addressing these problems early can prevent more serious damage to the bearings and associated components.
To sum it all up, grease ensures the smooth operation and longevity of various mechanical systems. By selecting the right grease and maintaining proper lubrication practices, you can significantly enhance the performance and reliability of your bearings, leading to longer equipment life and reduced maintenance costs. When handling NBC Bearings always refer to the manufacturing guide to ensure you follow the best practices applicable to your bearings to ensure the longevity of your bearings with minimal downtime.
FAQ's
What grease is used for bearings?
Various types of grease, including lithium-based, synthetic, and specialty greases, are used in bearings depending on the application.
What grease is used in industry?
In industrial settings, synthetic and lithium-based greases are commonly used due to their durability and ability to withstand harsh conditions.
What are the uses of grease?
Grease is used to lubricate, protect against corrosion, and reduce friction in bearings and other mechanical components.
What is the chemical name of grease?
Grease does not have a single chemical name, as it is a combination of base oil, thickener, and additives.
What is the full form of EP2 grease?
EP stands for “Extreme Pressure,” and EP2 grease is designed to withstand high-pressure conditions.
What is Type A grease?
Type A grease is a specific formulation used in certain automotive and industrial applications, known for its water resistance and thermal stability.