In the realm of industrial automation, bearings play a pivotal role in enabling smooth and efficient operation across a myriad of automated systems. From precision motion control to supporting heavy loads, bearings are indispensable components that facilitate the seamless functioning of automated machinery and processes.
Understanding Bearings in Industrial Automation:

Motion Control
Bearings ensure smooth and low-friction movement between rotating or moving parts. They allow components to rotate or translate with minimal resistance, facilitating accurate positioning and trajectory control in automated machinery and systems. By enabling precise motion, the machinery will achieve accuracy, repeatability, and overall enhanced performance.
Reduced Friction
One of the primary functions of bearings is to minimise friction between moving parts within automated systems. This is successfully achieved by
- incorporating rolling elements like balls or rollers
- reducing the contact area and frictional forces between components
- enhancing smoother movement leads to improved energy efficiency
- reduced wear and tear on mechanical parts, prolongs the lifespan of bearings and makes automated systems more reliable.
Support Heavy Loads
Bearings are engineered to withstand and support heavy loads encountered in industrial automation applications. Depending on the type and configuration, bearings distribute loads evenly across their contact surfaces, thereby preventing excessive stress on individual components. For instance, roller bearings, such as cylindrical or spherical roller bearings, are designed to support radial and axial loads simultaneously, making them suitable for applications with heavy-duty requirements. By providing robust support, bearings ensure the stability, durability, and safety of automated machinery handling heavy loads.
To summarise, bearings serve multiple functions in the context of industrial automation. In automated systems,
- bearings enable precise movement and positioning of machine components
- bearings ensure accuracy and repeatability in manufacturing processes
- bearings minimise friction between moving parts
- bearings contribute to energy efficiency
- bearings prolong the lifespan of machinery
Selecting the right bearings for specific automation applications is essential to optimise performance and reliability.
Types of Bearings Used in Industrial Automation
In industrial automation, several types of bearings are commonly used, each offering unique characteristics and advantages suited to specific application requirements:

Ball Bearings
Ball bearings feature rolling elements, typically spherical balls, sandwiched between inner and outer rings. They are known for their high-speed capability, low friction, and smooth operation.
Advantages:
- Low friction: Ball bearings reduce friction between rotating components, enabling efficient motion and energy savings.
- High-speed capability: Their design allows for high rotational speeds, making them ideal for applications requiring rapid motion.
- Low noise and vibration: Ball bearings operate quietly and smoothly, contributing to a quieter working environment.
Suitable Applications:
- Precision machinery: Ball bearings are commonly used in robotics, CNC machines, and servo systems where precise motion control is essential.
- Conveyor systems: They are suitable for conveying applications that require smooth and continuous movement.
Roller Bearings
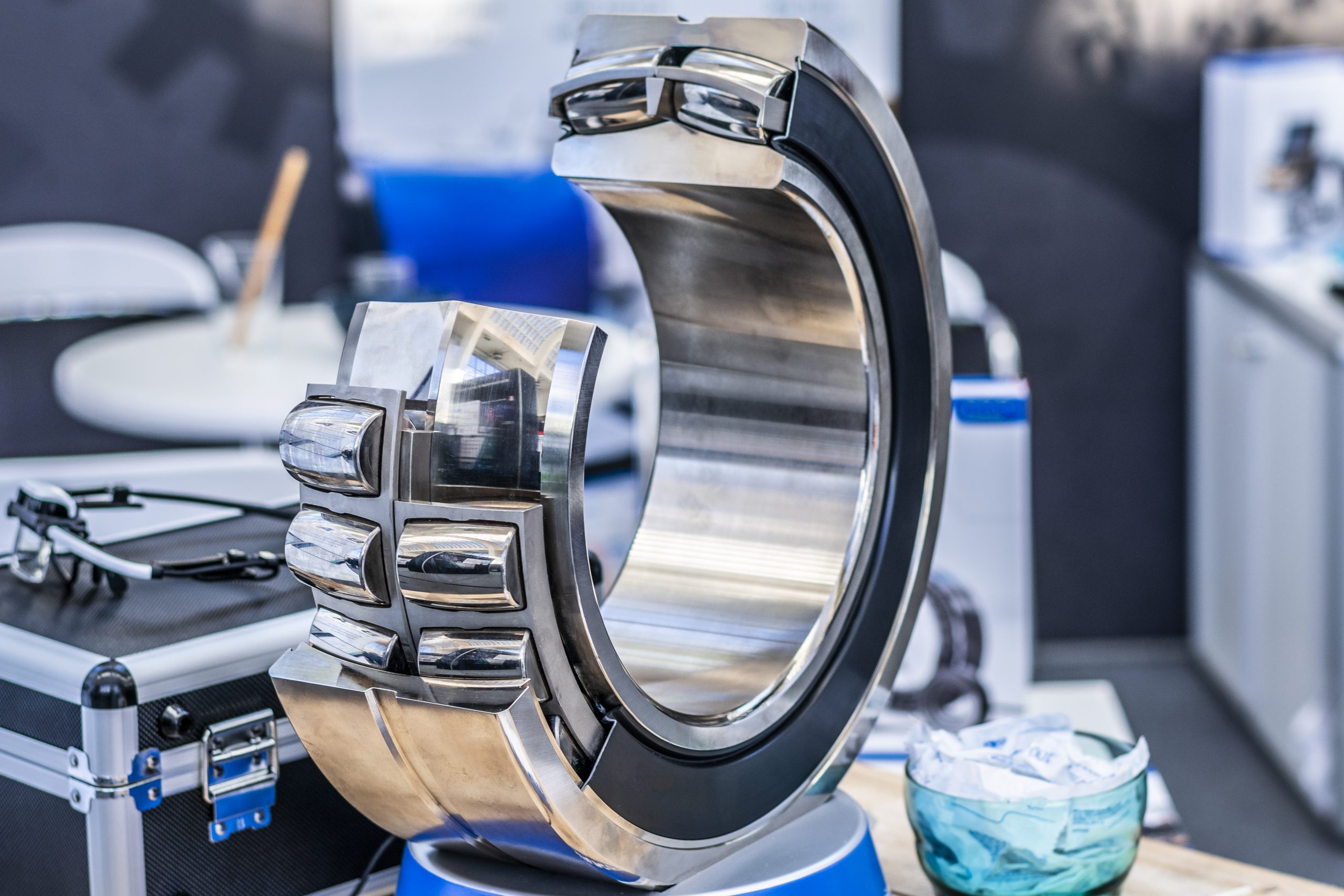

Roller bearings utilise cylindrical, tapered, or spherical rollers instead of balls. They offer higher load-carrying capacity and improved shock resistance compared to ball bearings.
Advantages:
- High load capacity: Roller bearings can withstand heavier loads and provide enhanced support, making them suitable for applications with significant axial or radial loads.
- Improved shock resistance: The larger contact area between rollers and raceways enhances shock absorption, making roller bearings ideal for applications with dynamic loading conditions.
- Increased rigidity: Roller bearings exhibit greater rigidity and stability under heavy loads, ensuring precise positioning and motion control.
Suitable Applications:
- Heavy machinery: Roller bearings are commonly used in industrial robots, machine tools, and material handling equipment handling heavy loads.
- Automotive industry: They find applications in vehicle transmissions, wheel hubs, and suspension systems due to their robustness and load-carrying capacity.
Linear Bearings
Linear bearings facilitate linear motion along a guided path, eliminating rotational motion. They include various types such as ball bushings, roller bushings, and linear guides.
Advantages:
- Smooth and precise motion: Linear bearings offer precise linear motion with minimal friction, ensuring accurate positioning in automated systems.
- Low maintenance: They typically require minimal lubrication and maintenance due to their simple design, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Compact and lightweight: Linear bearings are often compact and lightweight, making them suitable for applications with space constraints or weight limitations.
Suitable Applications:
- CNC machining: Linear bearings are used in CNC routers, milling machines, and 3D printers to provide smooth and precise movement along linear axes.
- Packaging and handling systems: They are employed in conveyor belts, pick-and-place machines, and robotic arms for linear motion control in packaging and material handling operations.
To summarise,
- Ball bearings are prized for their high-speed capabilities and low friction, making them ideal for applications requiring rapid motion and precise positioning.
- Roller bearings excel in supporting heavy radial and axial loads.
- Plain bearings provide reliable performance in applications with oscillating or linear motion.
Bearings in Motion Control Systems
Precision motion control systems are critical components in industrial robots and CNC machines, where precise positioning and movement are essential for accurate operations.
These systems rely on bearings to facilitate smooth and controlled motion along multiple axes, enabling precise tool or end-effector positioning and trajectory control. Bearings play a crucial role in minimising friction and backlash, ensuring that the motion control system responds accurately to input commands and maintains tight tolerances.
How do bearings improve their performance?
- Bearings enable the smooth rotation of motor shafts and lead screws, translating rotary motion into linear motion in CNC machines and robots.
- Bearings support the moving parts of linear guides, such as rails and carriages, providing low-friction movement and precise positioning along the axes.
- Bearings reduce vibrations and resonance, contributing to improved stability and accuracy during high-speed machining or robotic operations.
- Minimised friction and wear enhance the longevity and reliability of precision motion control systems, reducing maintenance requirements and downtime.
Examples of Bearing Applications in Industrial Automation
- Precision angular contact ball bearings are commonly used in spindle assemblies of CNC machines, to support high-speed rotation and provide axial stiffness for accurate machining operations.
- Precision motion control systems, such as those utilised in industrial robots and CNC machines, heavily rely on bearings to achieve accurate and repeatable movement. In these systems
- Linear ball bearings and profiled rail guides enable precise linear motion along the X, Y, and Z axes of CNC machines, ensuring accurate tool positioning and machining.
- Industrial robots utilise various types of bearings, including cross-roller bearings and angular contact ball bearings, in their joints and actuators to facilitate smooth and precise movement for tasks such as pick-and-place operations and assembly tasks.
Whether it’s the articulated joints of a robotic arm or the linear slides of a CNC machine, bearings ensure smooth motion and optimal performance. At NBC Bearings, our Research & Development department continually innovates to develop custom bearing solutions tailored to the unique requirements of precision motion control systems, further optimising performance and efficiency in industrial automation applications.
Bearings in Conveyor Systems:
Bearings play a crucial role in conveyor systems, which are widely used in industrial automation for material handling and product transportation. These systems rely on bearings to support rotating components such as rollers, pulleys, and shafts, enabling smooth and efficient movement of conveyor belts and carrying heavy loads with minimal friction.
- Bearings are used in conveyor rollers to support the weight of conveyed materials and provide low-friction rotation, ensuring smooth movement along the conveyor path.
- They facilitate the transfer of power from drive components, such as motors or gearboxes, to conveyor pulleys, allowing the belt to move at the desired speed and direction.
- Bearings in conveyor systems help reduce energy consumption by minimising friction losses, contributing to overall system efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Sealed and self-lubricating bearings offer improved reliability and longevity in conveyor applications by protecting against contamination and reducing maintenance requirements.
- Bearings with enhanced load-carrying capacities and corrosion resistance are ideal for harsh operating environments, such as those found in mining, manufacturing, and logistics industries.
- Integration of precision bearings with conveyor components, such as idler rollers and tensioners, ensures precise alignment and tracking of the conveyor belt, minimising downtime and enhancing productivity.
Some bearings which help address the above outcomes are:
- Deep groove ball bearings and spherical roller bearings support radial and axial loads while providing smooth rotation under heavy loads.
- Pillow block bearings and flanged units support conveyor shafts and pulleys, providing reliable performance and easy installation in various conveyor configurations.
- Ceramic or corrosion-resistant bearings are employed in conveyor systems handling abrasive materials or operating in corrosive environments, ensuring long-term reliability and reduced maintenance costs.
Bearings in Robotics and Automated Machinery
- Bearings enable precise movement and manipulation of robotic arms, end effectors, and tooling systems.
- Bearings support the articulated joints and rotary actuators of industrial robots, allowing for agile and dexterous movement in assembly, welding, and material handling tasks.
- Bearings facilitate the smooth operation of automated machinery, such as pick-and-place systems, CNC machining centres, and 3D printers, enhancing productivity and efficiency in manufacturing operations.
Some bearings which help address the above outcomes are:
- Ceramic bearings, which offer superior performance in high-speed and high-temperature environments.
- Magnetic bearings, which provide frictionless motion and maintenance-free operation.
- Integrated bearing units incorporating sensors and condition monitoring capabilities to enable predictive maintenance, reduce downtime and optimise equipment reliability.
To conclude, bearings are indispensable components that underpin the smooth operation and efficiency of automated systems. From precision motion control in robotics to conveying materials in manufacturing facilities, bearings play a crucial role in diverse applications across various industries. By understanding the functions, types, and applications of bearings in industrial automation, engineers and practitioners can optimise performance, enhance reliability, and drive innovation in automated processes and machinery.
FAQ's
Which type of bearing is used in industry automation?
Ball bearings, roller bearings, and plain bearings are commonly used in various industrial applications, offering distinct advantages based on specific requirements.
What is an industrial bearing?
An industrial bearing is a mechanical component used to support rotating or moving parts within industrial machinery and equipment, facilitating smooth motion and reducing friction.
What are industrial bearings used for?
Industrial bearings are used in a wide range of applications, including conveyors, robotics, CNC machines, automotive manufacturing, and aerospace systems, to enable smooth movement, reduce friction, and support heavy loads.
What is the use of bearing in industry automation?
Bearings play a crucial role in industrial machinery by supporting rotating shafts, axles, and components, enabling smooth motion, reducing friction, and ensuring reliable operation of automated systems.