Bearing housings and bushings are essential components in machinery that support and align rotating shafts or axles.
What are Bearing Housings and Bushings?
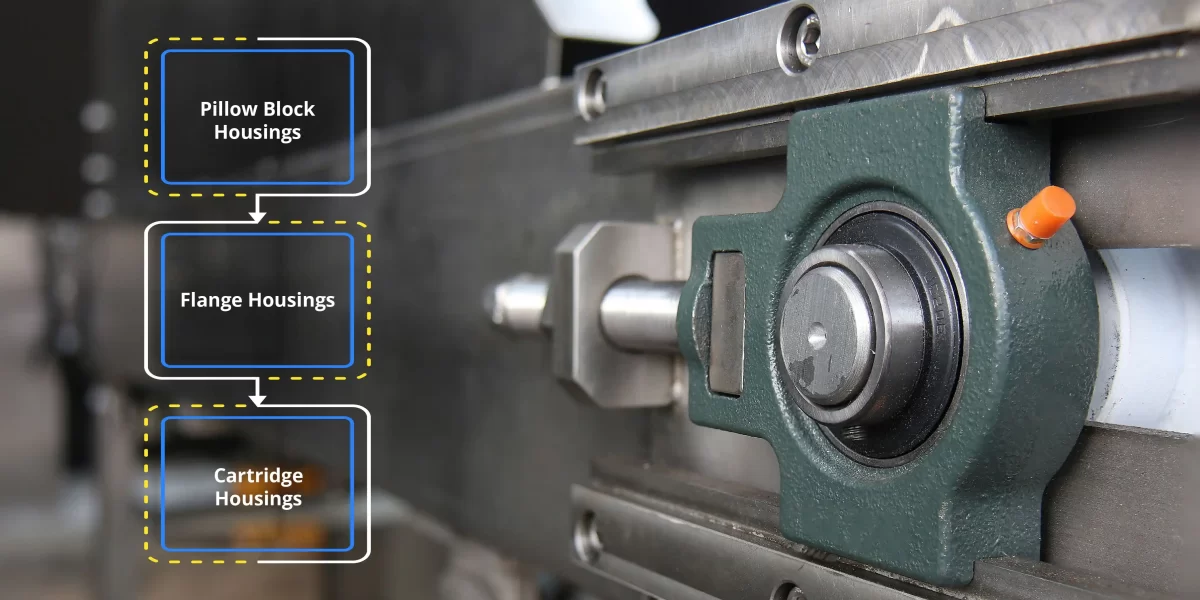
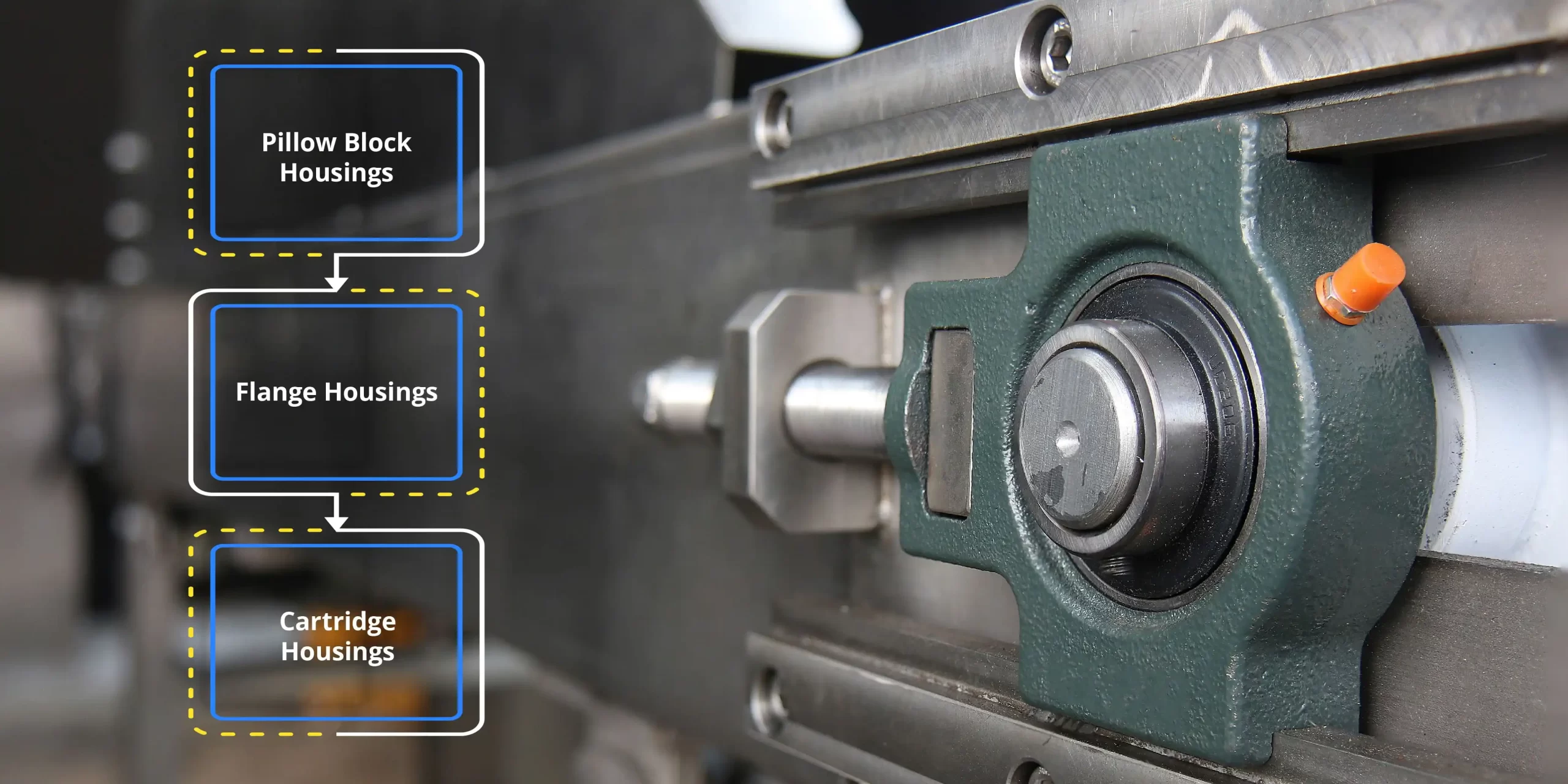
Bearing housings are typically made of materials such as metal, plastic, or composite, and they come in various types, including pillow block, flange, and cartridge housings.
- They provide a stable mounting surface for bearings.
- They eliminate friction and enhance longevity of equipment and machinery across sectors.
- They also ensure proper alignment for smooth operation.
Bushings, on the other hand, are cylindrical sleeves that provide a bearing surface for shafts, reducing friction and wear.
- They provide reliable, low-friction support and alignment for moving parts in industrial machinery and equipment.
- They contribute to the efficiency, durability, and safety of mechanical systems across a wide range of industries.
Choosing the right bearing housing and bushing is crucial for optimizing machinery performance and ensuring its long-term reliability.
Types of Bearing Housings and Bushings
There are several types of housings, each designed to meet specific application requirements and operating conditions:
- Pillow Block Housings: These are the most common type of bearing housings, featuring a pedestal or base with a mounting surface for the bearing. Pillow block housings are widely used in conveyor systems, agricultural machinery, and industrial equipment.
- Flange Housings: Flange housings have a flat surface with holes for mounting bolts, allowing the bearing to be attached directly to a structure or machine frame. They are commonly used in applications where space is limited or where precise alignment is required.
- Cartridge Housings: Cartridge housings consist of a cartridge unit that contains the bearing and seals, making installation and maintenance easier. They are often used in applications such as pumps, compressors, and gearboxes.
Some of the most common types of bushings include
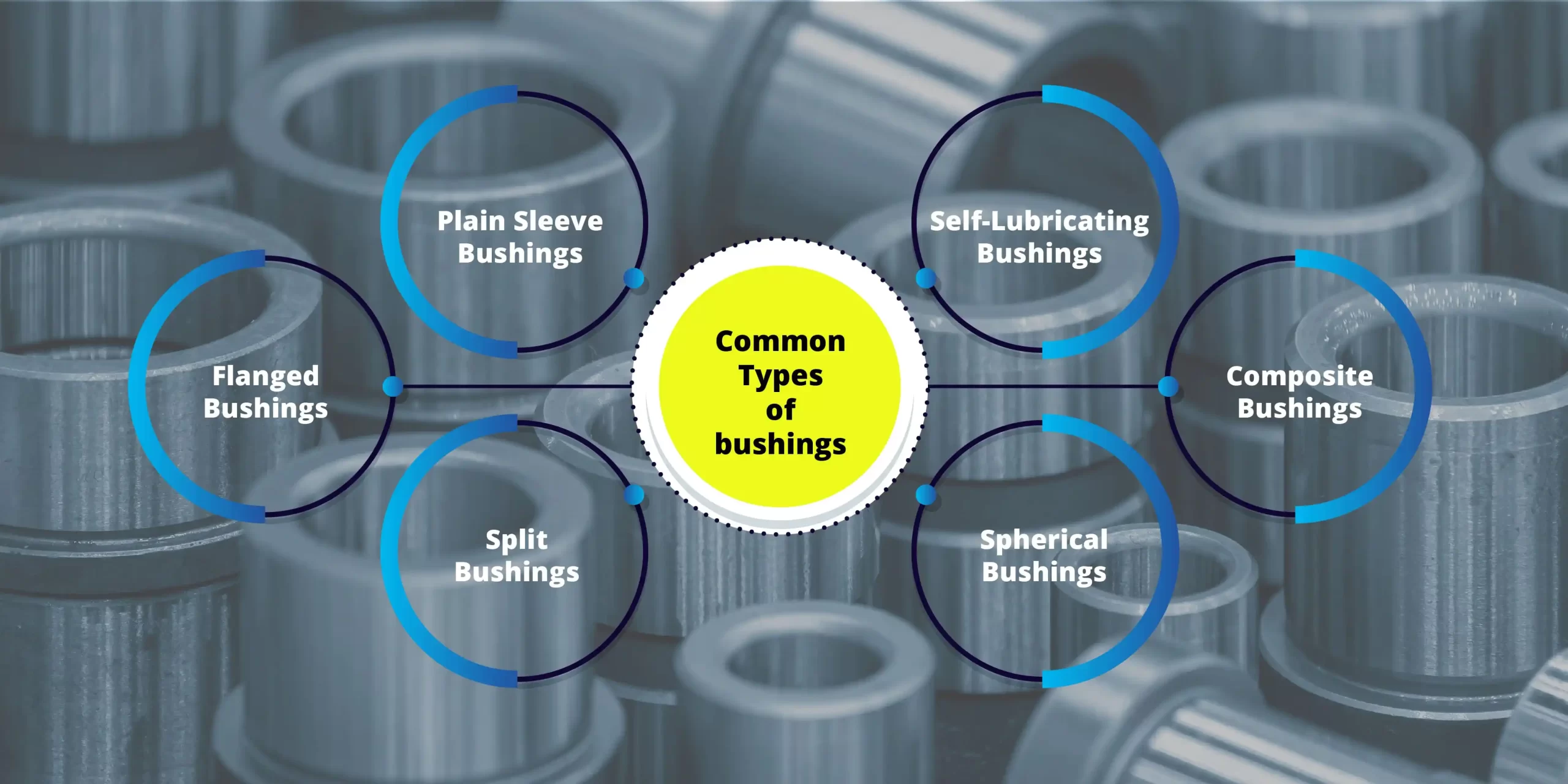
- Plain Sleeve Bushings: Plain sleeve bushings, also known as cylindrical bushings or sleeve bearings, consist of a cylindrical metal sleeve with a smooth inner surface. They are typically made from materials such as bronze, brass, or steel and provide low-friction support for rotating shafts or axles. Plain sleeve bushings are used in a wide range of applications, including motors, pumps, and industrial machinery.
- Flanged Bushings: Flanged bushings have an additional flange or collar at one end to provide axial support and retention within a housing or mounting surface. The flange helps prevent axial movement and facilitates easy installation and removal of the bushing. Flanged bushings are commonly used in applications where axial retention is required, such as in automotive suspension systems and conveyor rollers.
- Split Bushings: Split bushings, also known as split sleeve bushings or split bearings, are designed to accommodate easy installation and removal without the need to disassemble machinery or shafts. They feature a longitudinal split along their length, allowing them to be installed or removed by sliding them onto or off a shaft or housing. Split bushings are often used in applications where access is limited or where frequent maintenance is required.
- Self-Lubricating Bushings: Self-lubricating bushings incorporate solid lubricants or lubricating compounds embedded within the material matrix, reducing the need for external lubrication. These bushings offer low-friction performance and extended service life, making them ideal for applications where regular lubrication is impractical or challenging. Self-lubricating bushings are commonly used in automotive suspension systems, industrial equipment, and aerospace applications.
- Composite Bushings: Composite bushings are made from a combination of materials, such as polymers, fibers, and fillers, to achieve specific performance characteristics. They offer advantages such as corrosion resistance, low friction, and vibration damping, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Composite bushings are used in automotive suspension systems, marine equipment, and recreational vehicles, among other applications.
- Spherical Bushings: Spherical bearings, also known as spherical bushings or spherical plain bearings, have an inner ring with a spherical or convex outer surface and an outer ring with a corresponding concave inner surface. This design allows for angular misalignment and accommodates axial and radial loads simultaneously. Spherical bearings are used in applications where oscillating or tilting movements are present, such as in automotive suspension systems, construction equipment, and industrial machinery.
Materials Used and Their Properties:
Bearing housings and bushings can be made from various materials, each offering unique properties suited to different applications.
- Metal housings, such as cast iron or steel, provide excellent strength and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications.
- Plastic housings offer corrosion resistance and are lightweight, making them ideal for applications where weight is a concern or where exposure to harsh chemicals is a possibility.
- Composite materials, such as fiberglass-reinforced polymers, offer a combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and weight savings, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Factors Influencing Selection
- Load Capacity and Type of Load: The load capacity and type of load, whether radial, axial, or combined, are critical factors to consider when selecting bearing housings and bushings. Different types of housings and materials may be required to withstand varying load conditions.
- Operating Conditions: Operating conditions, including temperature, speed, and environmental factors, play a significant role in determining the suitability of bearing housings and bushings. Housings and bushings must be able to withstand the conditions they will be exposed to, whether it’s high temperatures, high speeds, or corrosive environments.
- Lubrication Requirements and Compatibility: Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation and longevity of bearing housings and bushings. Different types of lubricants may be required depending on the application and operating conditions. It’s essential to select housings and bushings that are compatible with the chosen lubrication method to ensure optimal performance and minimal maintenance requirements.
Maintenance of Bearing Housings and Bushings
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the continued performance and longevity of bearing housings and bushings.
- Set up & follow recommended lubrication schedules and methods to ensure proper lubrication of the bearings.
- Monitor common issues such as misalignment, overheating, or excessive wear, and taking corrective action as needed, to help prevent premature failure and costly downtime.
- Troubleshooting steps may include adjusting alignment, replacing worn components, or addressing environmental factors that may be affecting performance.
In conclusion, choosing the right bearing housing and bushing is essential for optimizing machinery performance and ensuring its long-term reliability. By understanding the different types of housings and materials available, as well as the factors influencing selection and maintenance considerations, engineers and maintenance professionals can make informed decisions to meet the needs of their applications effectively.
FAQ's
What is the function of bearing housing in a pump?
The bearing housing in a pump provides support and alignment for the pump shaft and bearings, ensuring smooth operation and reducing vibration and noise.
What are housed bearings?
Housed bearings are bearings that are mounted in a bearing housing, providing support and alignment for rotating shafts or axles in machinery.
What are the two basic bearing housings?
The two basic types of bearing housings are pillow block housings and flange housings, each offering different mounting configurations and features.
What is the best material for bearing housing?
The best material for bearing housing depends on the specific application requirements, including load capacity, operating conditions, and environmental factors. Metal housings, such as cast iron or steel, are commonly used for their strength and durability, but plastic and composite materials may be suitable for applications where corrosion resistance or weight savings are priorities.
How to design bearing housing?
Designing a bearing housing involves considering factors such as load capacity, operating conditions, and mounting requirements, as well as selecting the appropriate material and configuration to ensure proper support and alignment for the bearing. Working with experienced engineers or consulting industry standards and guidelines can help ensure the successful design of bearing housings for specific applications.