Bearing cages are essential components in the operation of rolling element bearings. They play a pivotal role in maintaining the spacing of rolling elements (like balls or rollers), guiding their motion, and reducing friction. Without bearing cages, the rolling elements would cluster together, leading to increased friction, heat, and wear, ultimately resulting in premature bearing failure.
Types of Bearing Cages

There are several types of bearing cages, each designed to cater to specific applications and operational conditions. Understanding the differences between these types can help in selecting the right bearing cage for your needs.
| Type of Bearing | Description | Features | Applications |
| Stamped Steel Cages | These cages are made from thin sheets of steel, which are stamped and formed into shape. | High strength, Light-weight, Cost-effective. | Commonly used in automotive and industrial machinery where durability and cost efficiency are crucial. |
| Machined Brass Cages | These cages are machined from solid brass. | Excellent durability, resistance to corrosion, and ability to handle high loads. | Ideal for heavy-duty applications such as mining equipment and heavy machinery. |
| Polyamide Cages | Made from high-strength polymers, often reinforced with fibers. | Lightweight, low friction, and resistant to many chemicals. | Used in applications requiring low weight and high-speed capabilities, such as in aerospace and consumer electronics. |
| Crown Cages | Also known as “snap-in” cages, they have a unique design that snaps into place. | Simplifies assembly and provides excellent guidance for rolling elements. | Frequently used in high-speed applications where precise alignment is necessary. |
Materials Used in Bearing Cages
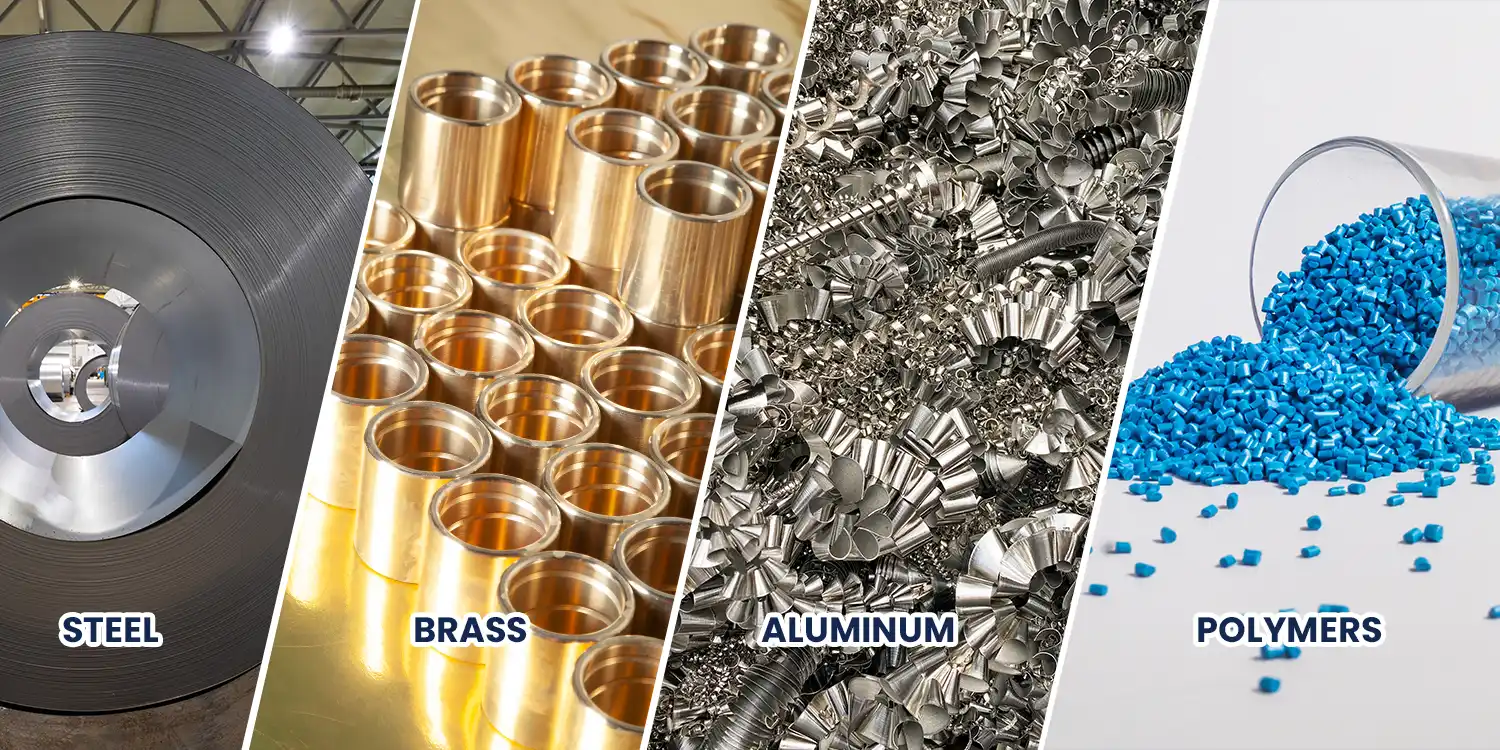

Bearing cages are manufactured from a variety of materials, each offering distinct advantages depending on the application and operating environment.
Steel
- High strength, durability and wear resistance.
- Ideal for heavy-duty and high-load applications.
Brass
- Excellent corrosion resistance good machinability and high load-bearing capacity.
- Suitable for harsh environments and heavy machinery.
aluminium
- Lightweight, good thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
- Used in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aerospace.
Design Considerations for Bearing Cages
Several factors influence the design of bearing cages, ensuring they meet the specific requirements of different applications.
- Cage Geometry: The geometry of the cage is critical to maintaining the correct spacing and alignment of the rolling elements within the bearing. Properly optimized cage geometry reduces weight while ensuring the strength and stability needed to handle operational loads.
- Strength and Durability: The material used for the cage must provide sufficient strength to handle the operational stresses without deforming or failing. Common materials include steel, brass, aluminum, and high-strength polymers.
- Lubrication Requirements: Proper lubrication reduces friction and wear, extending the bearing’s life. Cages often incorporate features such as lubrication channels or reservoirs to ensure that the rolling elements and raceways receive adequate lubrication. The design should facilitate the easy application of lubricants and maintain optimal lubrication conditions throughout the bearing’s life.
- Manufacturing Precision: High manufacturing precision ensures that the cages fit correctly and function as intended. Tight tolerances must be maintained during the manufacturing process to ensure that the cages provide proper alignment and spacing of the rolling elements. This includes dimensional accuracy, surface finish quality, and consistency in production.
- Weight Considerations: In high-speed and lightweight applications, the weight of the cage can significantly impact performance. Lighter materials like polyamide or aluminum can be used to reduce the overall weight of the bearing without compromising strength.
- Noise and Vibration: Excessive noise and vibration can indicate issues with the bearing and reduce the lifespan of the machinery.Cage designs that reduce contact between rolling elements and minimize friction can help in lowering noise and vibration levels
By carefully considering these design factors, bearing manufacturers can produce cages that meet the specific needs of various applications, ensuring reliability, efficiency, and longevity of the bearings. Understanding and optimizing these aspects is crucial for engineers and designers working in industries where bearings play a vital role in machinery and equipment performance.
Manufacturing Processes for Bearing Cages
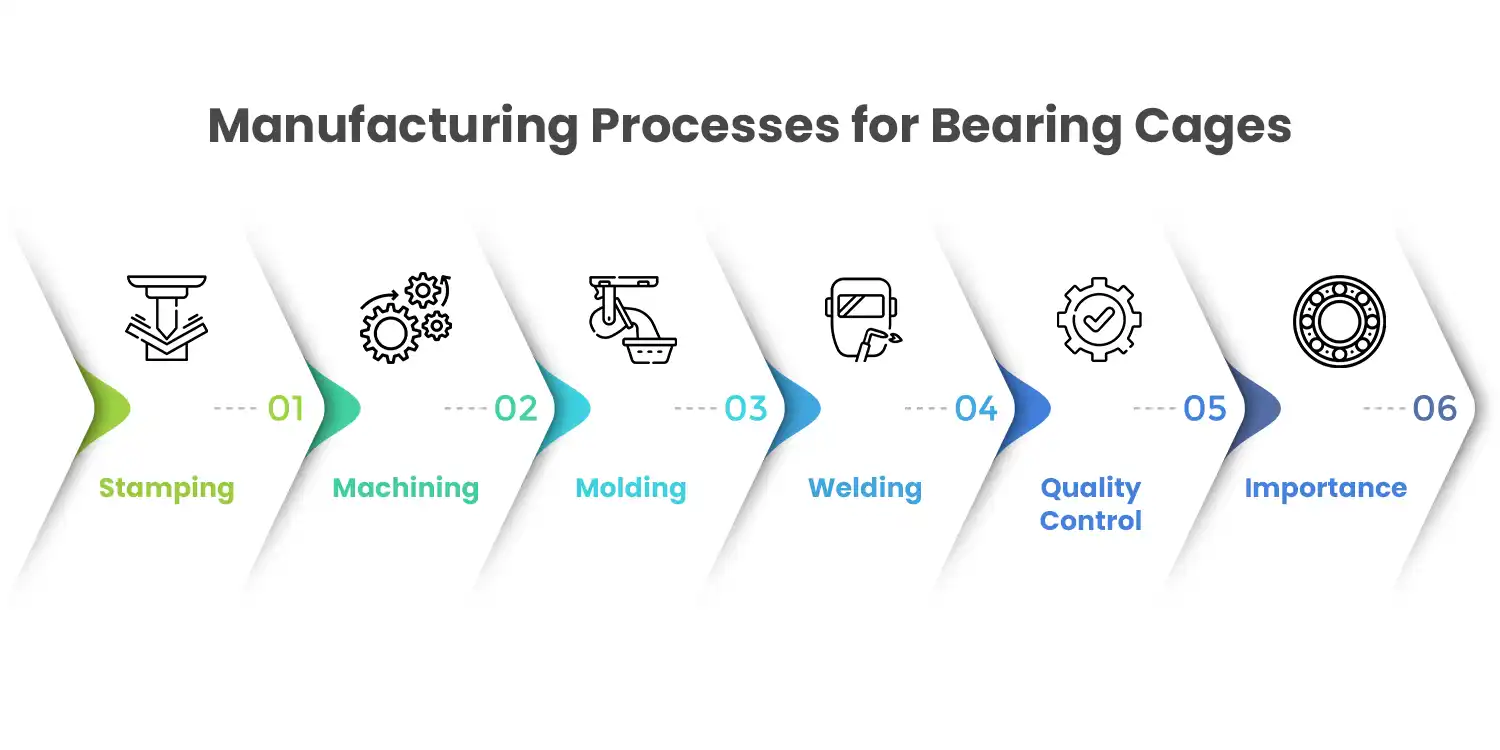
The production of bearing cages involves various processes to ensure high quality and precision.
Stamping
- Process: Thin metal sheets are stamped into shape using high-pressure dies.
- Applications: Common for producing stamped steel cages.
Machining
- Process: Solid materials are machined into the desired shape using CNC machines.
- Applications: Used for brass and aluminum cages where precision is critical.
Molding
- Process: Polymers are molded into shape using injection molding.
- Applications: Ideal for producing polyamide cages.
Welding
- Process: Components are welded together to form the final shape.
- Applications: Sometimes used for complex cage designs.
Quality Control
- Measures: Dimensional inspections, material testing, and load testing.
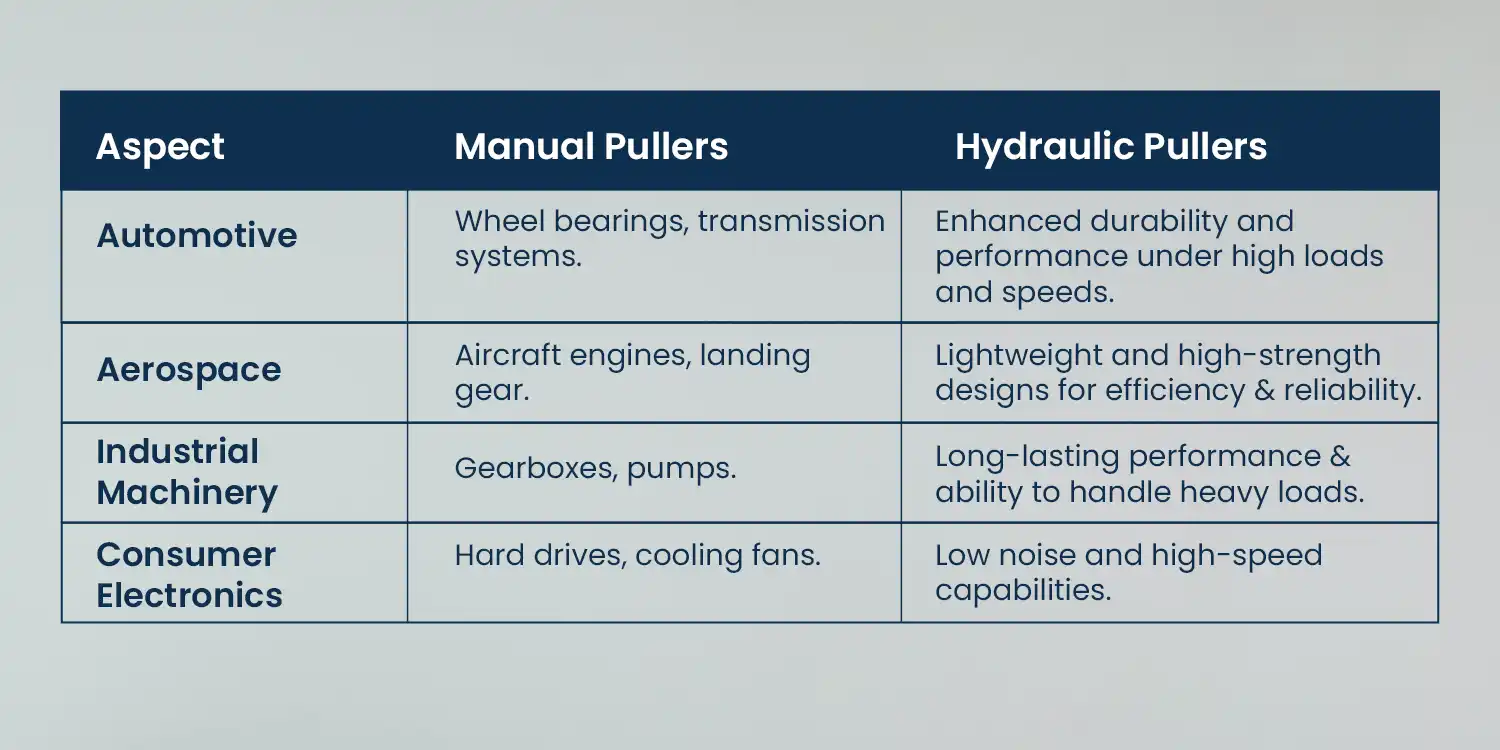
Applications of Bearing Cages
Maintenance of Bearing Cages
Proper maintenance extends the life of bearing cages and prevents premature failure. Here are some of the most commonly implemented best practices for regular maintenance:
- Regular Inspection: Check for signs of wear, damage, or lubrication issues.
- Lubrication: Follow recommended lubrication schedules and use appropriate lubricants.
- Cleaning: Keep bearings clean to prevent contamination and wear.
Over time, while noting down exceptions we will arrive at replacements as well. Here are some of the Replacement Guidelines followed:
- Signs of Wear: Replace bearings showing significant wear or damage.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect bearings and cages for signs of degradation.
- Procedure: Follow manufacturer guidelines for replacement to ensure proper fit and performance.
Conclusion
Bearing cages are fundamental to the efficient operation of rolling element bearings, providing essential support in maintaining spacing, reducing friction, and guiding motion. Understanding the different types, materials, design considerations, and applications of bearing cages can help in selecting the right components for specific needs, ultimately enhancing bearing performance and longevity. By keeping up with maintenance practices and embracing emerging trends in bearing technology, industries can ensure the reliability and efficiency of their machinery and equipment.
FAQ's
What is a cage in a bearing?
A cage, also known as a separator, is a component in a rolling element bearing that maintains the spacing between the rolling elements (balls or rollers). This helps in maintaining smooth rotation and extending the life of the bearing.
What materials are used in bearing cages?
Bearing cages are made from various materials including steel, brass, aluminum, and polymers. The choice of material depends on the specific application and operating conditions.
What is the purpose of a bearing cage or separator?
The primary purpose of a bearing cage or separator is to maintain the correct spacing between rolling elements within the bearing.
Do bearings need a cage?
Yes, most rolling element bearings require a cage to function efficiently. The cage ensures that the rolling elements are evenly spaced and do not contact each other, which reduces friction and wear.
What is the function of the cage?
The function of the cage in a bearing is to:
- Maintain proper spacing between rolling elements.
- Guide the rolling elements in their path.
- Reduce friction and wear.
- Enhance the overall stability and performance of the bearing.
What is a bearing without a cage called?
A bearing without a cage is typically referred to as a “full complement bearing.” In these bearings, the rolling elements are packed closely together, maximizing the bearing’s load-carrying capacity.
How is a bearing cage manufactured?
Bearing cages are manufactured using various processes, including stamping, machining, molding, and welding.