In electrical systems and rotating machinery, shaft grounding devices play a crucial role in maintaining equipment reliability and preventing bearing failure. These devices are designed to mitigate electrical currents that can otherwise cause significant damage to bearings and other critical components. Understanding the importance of shaft grounding devices is essential for anyone involved in the maintenance and operation of electrical and mechanical systems.
- Shaft grounding devices are essential in protecting rotating machinery from electrical damage.
- They provide a low-resistance path for electrical currents, preventing them from passing through the bearings.
- This is crucial because electrical discharges through bearings can cause pitting, fluting, and premature failure.
- Electrical currents can build up on rotating shafts due to various factors, including static electricity, electromagnetic induction, and residual currents from electrical systems.
- Shaft grounding devices effectively divert these currents away from the bearings, ensuring smooth and reliable operation.
Types of Shaft Grounding Devices
Several types of shaft grounding devices are used to protect bearings and other components in rotating machinery. These include carbon brush grounding systems, shaft grounding rings, and insulated bearing systems. Each type has its unique features and applications.

- Carbon Brush Grounding Systems: Carbon brushes are used to conduct electrical currents from the rotating shaft to the ground. These brushes are made from high-conductivity carbon materials, ensuring efficient current transfer. Which is why they are commonly preferred in applications where continuous electrical contact is required.
- Shaft Grounding Rings: Shaft grounding rings, also known as shaft grounding brushes or rings, consist of conductive fibers or wires that encircle the shaft. These rings provide a continuous low-resistance path for electrical currents to the ground, protecting the bearings from electrical damage. They are widely used in industrial applications due to their reliability and ease of installation.
- Insulated Bearing Systems: Insulated bearings are designed to prevent electrical currents from passing through the bearings by incorporating insulating materials between the bearing components. This type of grounding device is particularly useful in applications where direct grounding of the shaft is not feasible.
Benefits and Applications
Shaft grounding devices offer numerous benefits, including improved equipment reliability, extended bearing life, and reduced maintenance costs. They are widely used in various industries to protect critical machinery and ensure smooth operation.

Benefits
- Improved Equipment Reliability: By preventing electrical currents from passing through the bearings, shaft grounding devices enhance the reliability of rotating machinery. This leads to fewer unexpected breakdowns and increased uptime.
- Extended Bearing Life: Electrical damage can significantly reduce the lifespan of bearings. Shaft grounding devices protect bearings from electrical pitting and fluting, thereby extending their operational life.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: With fewer bearing failures and reduced wear and tear, maintenance costs are significantly lowered. This results in cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Applications:
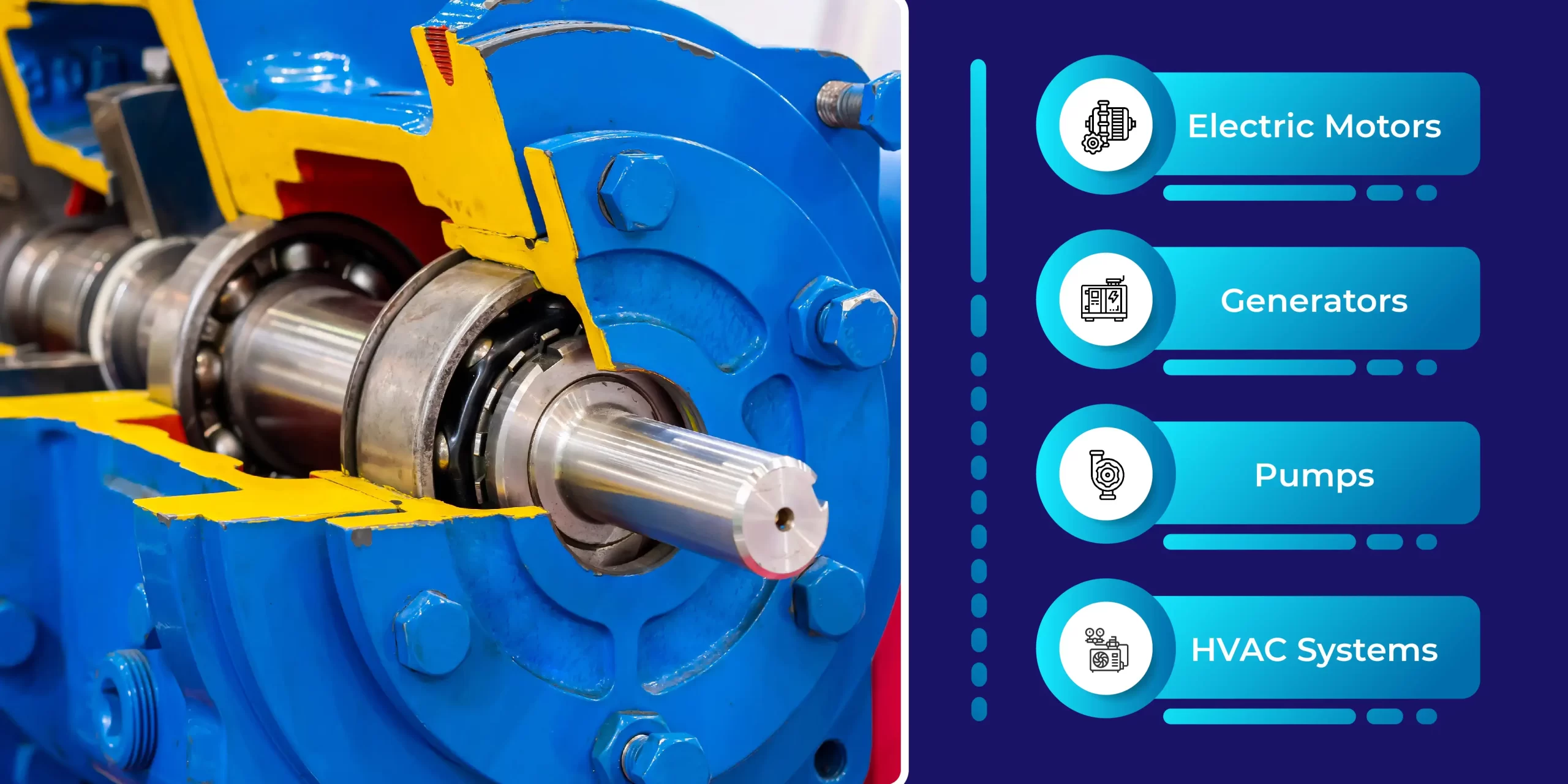
- Electric Motors: Shaft grounding devices are commonly used in electric motors to protect bearings from electrical damage caused by electromagnetic induction and residual currents.
- Generators: In generators, shaft grounding devices prevent electrical currents from damaging bearings, ensuring reliable power generation.
- Pumps: Pumps used in industrial applications benefit from shaft grounding devices by reducing bearing wear and extending the life of the equipment.
- HVAC Systems: In HVAC systems, shaft grounding devices protect bearings in fans and blowers from electrical damage, ensuring efficient operation.
| Applications | Benefits |
| Electric Motors | Enhanced reliability, extended bearing life |
| Generators | Reliable power generation |
| Pumps | Reduced bearing wear, extended equipment life |
| HVAC Systems | Efficient operation, reduced maintenance costs |
Design Considerations and Selection

Selecting the appropriate shaft grounding device involves considering several factors, including shaft size, operating conditions, and environmental factors. Proper selection ensures optimal performance and protection of the bearings.
- Shaft Size: The diameter and length of the shaft influence the type of grounding device required. For example, larger shafts may require multiple grounding rings or brushes to ensure effective current diversion.
- Operating Conditions: The operating environment, including temperature, humidity, and the presence of contaminants, affects the choice of grounding device. Some devices are better suited for harsh environments, while others are designed for cleaner, controlled settings.
- Environmental Factors: Factors such as vibration, dust, and moisture can impact the performance of grounding devices. It is essential to choose devices that are durable and resistant to environmental challenges.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and regular maintenance of shaft grounding devices are critical to their effectiveness. Following best practices ensures optimal performance and long-term protection of the bearings.
Installation Guidelines:
- Ensure Clean Surfaces: Before installation, ensure that the shaft and grounding device surfaces are clean and free from contaminants. This ensures efficient current transfer and prevents potential damage.
- Proper Alignment: Align the grounding device correctly with the shaft to ensure continuous contact. Misalignment can lead to ineffective grounding and increased wear.
- Secure Fastening: Use appropriate fasteners to secure the grounding device in place. Ensure that it remains firmly attached during operation to prevent movement and loss of contact.
Maintenance Best Practices:
- Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect the grounding device for signs of wear, damage, or contamination. Replace worn or damaged components to maintain optimal performance.
- Cleanliness: Keep the grounding device and shaft clean to ensure efficient current transfer. Regular cleaning prevents the buildup of dust and debris that can impair performance.
- Lubrication: In some cases, applying a suitable lubricant can r
Conclusion
Shaft grounding devices are essential components in rotating machinery, playing a vital role in preventing bearing failure and ensuring reliable operation. By providing a low-resistance path for electrical currents, these devices protect bearings from electrical damage, extending their life and reducing maintenance costs. Understanding the different types of shaft grounding devices, their benefits, and proper installation and maintenance practices is crucial for anyone involved in the maintenance and operation of electrical and mechanical systems. By implementing effective shaft grounding solutions, industries can enhance the reliability and longevity of their critical machinery.
FAQ's
What is a shaft earthing device?
A shaft earthing device, also known as a shaft grounding device, is a component used in rotating machinery to divert electrical currents away from bearings. It provides a low-resistance path for electrical currents, preventing them from passing through the bearings and causing damage. Shaft earthing devices are essential for protecting bearings from electrical pitting and fluting, which can lead to premature failure and increased maintenance costs.
Is shaft grounding necessary?
Yes, shaft grounding is necessary in many rotating machinery applications to protect bearings from electrical damage. Electrical currents can build up on rotating shafts due to various factors, such as static electricity and electromagnetic induction. Without proper grounding, these currents can pass through the bearings, causing pitting, fluting, and premature failure. Shaft grounding devices provide a low-resistance path for these currents, ensuring the reliable operation and longevity of the machinery.
How do grounding brushes work?
Grounding brushes work by providing a continuous electrical contact between the rotating shaft and the ground. These brushes are made from high-conductivity carbon materials that can efficiently transfer electrical currents. When installed on the shaft, grounding brushes ensure that any electrical currents are diverted away from the bearings, preventing damage. The brushes are designed to maintain consistent contact with the shaft, even during rotation, ensuring effective grounding at all times.
What are shaft grounding rings?
Shaft grounding rings, also known as shaft grounding brushes or rings, are devices that encircle the rotating shaft and provide a low-resistance path for electrical currents. These rings are made of conductive fibers or wires that create a continuous electrical contact with the shaft. Shaft grounding rings are commonly used in industrial applications to protect bearings from electrical damage. They are easy to install and provide reliable grounding, ensuring the smooth operation and longevity of the machinery.
What is the prop shaft grounding?
Prop shaft grounding refers to the practice of grounding the propeller shaft in marine and automotive applications to prevent electrical damage to bearings and other components. Electrical currents can build up on the propeller shaft due to various factors, such as static electricity and electromagnetic induction. Prop shaft grounding devices provide a low-resistance path for these currents, ensuring they are safely diverted to the ground. This practice helps protect bearings and other critical components from electrical pitting and fluting, extending their operational life.